Cost-effective Experimental Design
Overview
This is an R Markdown document. For further clarification of this code, read Design and Sampling Plan Optimization for RT-qPCR Experiments in Plants: A Case Study in Blueberry by Die, Roman, Flores and Rowland. Front. Plant Sci. (2016) 7:271.
0. Dependencies
This document has the following dependencies:
library(dplyr)
1. Set the number of potential replicates (1 to X) for each of the sample processing steps
nsubject = 5
nrna = 4
nqpcr = 3
nrt=4
2. Build a general matrix of potential sampling plans (as dataframe)
c.subject = rep(c(1:nsubject),each=nrna*nrt*nqpcr)
c.rna =rep(rep(c(1:nrna),each=nrt*nqpcr),nsubject)
c.rt = rep(rep(c(1:nrt),each=nqpcr),nsubject*nrna)
c.qpcr = rep(rep(c(1:nqpcr),nrt),nrna*nsubject)
#Check that all columns are equal length
length(c.subject) == length(c.rna) & length(c.subject)== length(c.rt) & length(c.subject)== length(c.qpcr)
## [1] TRUE
#Build the dataframe of sampling plans
dat <- tbl_df(data.frame(subject =c.subject,RNA =c.rna,RT=c.rt,qPCR =c.qpcr))
3. Define a function to estimate the variance (or SD) of the mean Cq or “Total expected variation””
total.var = function(nsubject,nrna,nrt,nqpcr) {
mean.var <- rna/(nsubject*nrna) + rt/(nsubject*nrna*nrt) +
qpcr/(nsubject*nrna*nrt*nqpcr)
}
4. Enter the variation (or SD) observed from the pilot experiment
# Example 4A. Mean GOIs, Tissue = leaves
n.genes = 3
rna =(0.43+0.02+0.64) / n.genes
rt = (0.73+0.28+0.53) / n.genes
qpcr = (0.32+0.18+0.49) / n.genes
# Example 4B. Mean GOIs, Tissue = fruits
n.genes = 3
rna = (0.41+0.42+0.43)/n.genes
rt = (0.34+0.31+0.29)/n.genes
qpcr = (0.30+0.27+0.35)/n.genes
5. Estimate the total expected variation (mean Cq) per sampling plan and add those values to the data frame
dat <- mutate(dat, Total.Mean = round(total.var(subject,RNA, RT, qPCR),2))
6. Create a new variable (total number of replicates) and add those values to the data frame
dat <- mutate(dat,Total.Rep=subject*RNA*RT*qPCR)
7. Enter the unitary cost throughout sample processing
cost.sub = 50
cost.rna = 10
cost.RT = 3
cost.qPCR = 1
8. Estimate cost for each sampling plan and add those values to the data frame
meanDat <- mutate(dat, Sampling.Cost = subject*cost.sub + (RNA*subject*cost.rna) +
(RT*RNA*subject*cost.RT) + (qPCR*RT*RNA*subject*cost.qPCR)) %>%
arrange(Sampling.Cost, desc(Total.Rep), desc(Total.Mean)) %>%
select(Sampling.Cost, Total.Rep, Total.Mean, subject, RNA, RT, qPCR)
9. Enter the requirements for the actual experiment
time.points = 3
budget = 1000
10. Create an index to identify sampling plans limited by the available budget
ind <- which(meanDat$Sampling.Cost*time.points < budget)
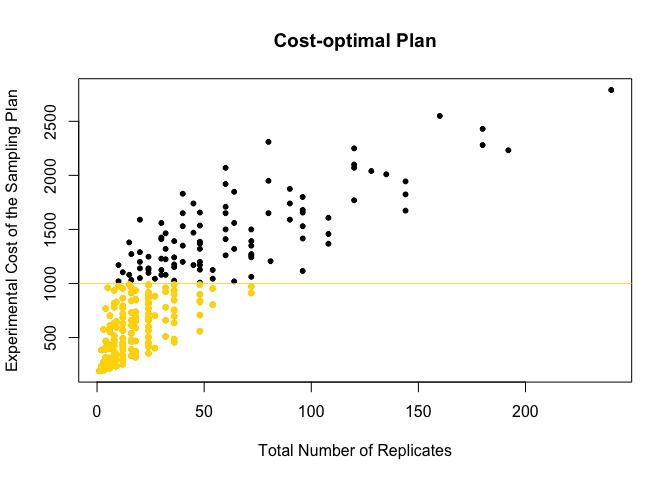
11. Plot the experimental plans and identifies those within the available budget
12. Get the sampling plan (out of those within the available budget) showing the minimum variance (or SD)
In other words: out of the different sampling plans, what is the minimum variance that we can find?
min.var <- min(meanDat[ind,3])
min.var
## [1] 0.07
13. Get and plot the sampling plan(s) showing the minimum variance (or SD)
#Get the sampling plan(s)
target = which(meanDat[ind,3] == min.var)
meanDat <- rename(meanDat, Cost.TP=Sampling.Cost)
meanDat[target,]
## Source: local data frame [5 x 7]
##
## Cost.TP Total.Rep Total.Mean subject RNA RT qPCR
## (dbl) (int) (dbl) (int) (int) (int) (int)
## 1 300 48 0.07 2 4 3 2
## 2 308 32 0.07 2 4 4 1
## 3 324 72 0.07 2 4 3 3
## 4 330 36 0.07 3 3 2 2
## 5 330 24 0.07 3 4 1 2
#Plot the sampling plan(s): identify plans with unique total number of replicates
plot(meanDat$Total.Rep, meanDat$Cost.TP*time.points, pch=20, main="Cost-optimal Plan",
xlab="Total Number of Replicates", ylab="Experimental Cost of the Sampling Plan")
points(meanDat$Total.Rep[ind], (meanDat$Cost.TP*time.points)[ind],
col="gold1", cex=0.8, bg="gold1", pch=21)
abline(h=budget, col="gold1",lwd=0.8)
points(meanDat$Total.Rep[target],
(meanDat$Cost.TP*time.points)[target],
col="cadetblue2", cex=1, bg="cadetblue2", pch=21)
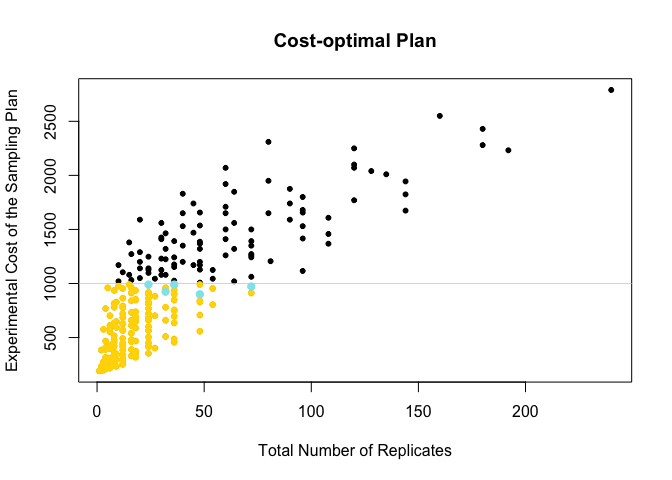
14. Get and plot the OPTIMAL PLAN (out of those showing the minimum variance)
#14.1 Criteria 1: plan that requires less final replicates
ind2 <- which(meanDat[target,2]==min(meanDat[target,2]))
#Find the optimal sampling plan
meanDat[target[ind2],]
## Source: local data frame [1 x 7]
##
## Cost.TP Total.Rep Total.Mean subject RNA RT qPCR
## (dbl) (int) (dbl) (int) (int) (int) (int)
## 1 330 24 0.07 3 4 1 2
Plot the optimal sampling plan accordingt to critera 14.1
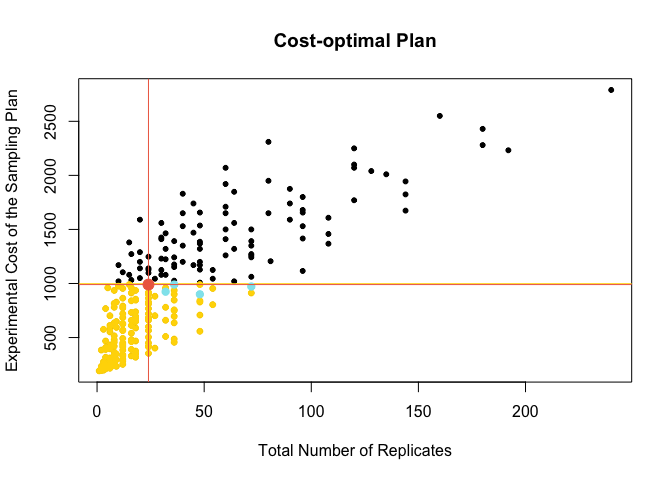
#14.2 Critera 2: plan that is least expensive
meanDat[target[1],]
## Source: local data frame [1 x 7]
##
## Cost.TP Total.Rep Total.Mean subject RNA RT qPCR
## (dbl) (int) (dbl) (int) (int) (int) (int)
## 1 300 48 0.07 2 4 3 2
Plot the optimal sampling plan according to criteria 14.2
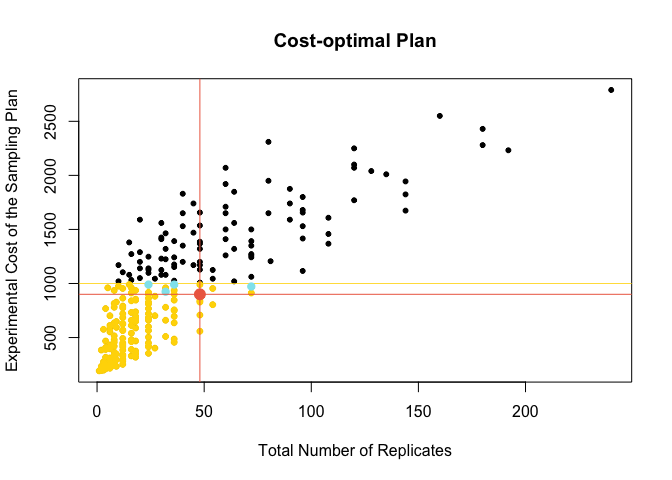
SessionInfo
\scriptsize
## R version 3.2.2 (2015-08-14)
## Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin13.4.0 (64-bit)
## Running under: OS X 10.10.5 (Yosemite)
##
## locale:
## [1] es_ES.UTF-8/es_ES.UTF-8/es_ES.UTF-8/C/es_ES.UTF-8/es_ES.UTF-8
##
## attached base packages:
## [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
##
## other attached packages:
## [1] dplyr_0.4.3
##
## loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
## [1] Rcpp_0.12.2 digest_0.6.8 assertthat_0.1 R6_2.1.1
## [5] DBI_0.3.1 formatR_1.2.1 magrittr_1.5 evaluate_0.8
## [9] stringi_1.0-1 lazyeval_0.1.10 rmarkdown_0.9 tools_3.2.2
## [13] stringr_1.0.0 yaml_2.1.13 parallel_3.2.2 htmltools_0.3
## [17] knitr_1.11
This document was processed on: 2016-02-11